-
Service
We strive to connect consumers with unbeatable pricing for wholesale pharmaceutical products. Our goal is to meet every customer’s expectations by creating a strong connection and understanding of their needs.
[button color=”blue” url=”http://www.url.com” size=”medium”]Deoxyribonucleic Acid[/button]
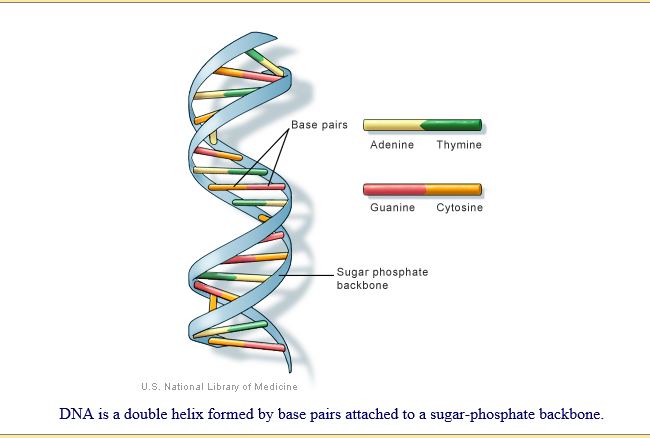
DNA contains the instructions needed for an organism to develop, survive and reproduce.
The answer lies in a molecule called deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), which contains the biological instructions that make each species unique. DNA, along with the instructions it contains, is passed from adult organisms to their offspring during reproduction.
Our DNA kits are used to determine Metabolism & Addictions for people.
Inside the nucleus of a cell, our genes are arranged along twisted, double-stranded molecules of DNA called chromosomes. In humans, each cell normally contains 23 pairs of chromosomes, for a total of 46. Twenty-two of these pairs, called autosomes, look the same in both males and females. The 23rd pair, the sex chromosomes, differ between males and females.
So, Chromosomes are the structures that hold our genes. Genes are the individual instructions that tell our bodies how to develop and function; they govern our physical and medical characteristics, such as hair color, blood type and susceptability to disease.
In this day in time, why wouldn’t you discover what’s going on in you’re body. Knowing about yourself is being proactive.
Available types of testing include:
Newborn screening: Newborn screening is used just after birth to identify genetic disorders that can be treated early in life.
Diagnostic testing: Diagnostic testing is used to diagnose or rule out a specific genetic or chromosomal condition. In many cases, genetic testing is used to confirm a diagnosis when a particular condition is suspected based on physical mutations and symptoms. The results of a diagnostic test can influence a person’s choices about health care and the management of the disease.
Carrier testing: Carrier testing is used to identify people who carry one copy of a gene mutation that, when present in two copies, causes a genetic disorder.
Prenatal diagnosis: Used to detect changes in a fetus’s genes or chromosomes before birth. This type of testing is offered to couples with an increased risk of having a baby with a genetic or chromosomal disorder.
Predictive and presymptomatic testing: Predictive and presymptomatic types of testing are used to detect gene mutations associated with disorders that appear after birth, often later in life. These tests can be helpful to people who have a family member with a genetic disorder, but who have no features of the disorder themselves at the time of testing.
-Predictive testing can identify mutations that increase a person’s chances of developing disorders with a genetic basis, such as certain types of cancer. For example, an individual with a mutation in BRCA1 has a 65% cumulative risk of breast cancer.
-Presymptomatic testing can determine whether a person will develop a genetic disorder, such as hemochromatosis (an iron overload disorder), before any signs or symptoms appear.
Pharmacogenomics: type of genetic testing that determines the influence of genetic variation on drug response.